The days of storing the most important information on flash drives and file cabinets are long gone. Modern-day storage involves storing massive amounts of sensitive data on the cloud. Whether it is family photos, videos, health documents, or employment files, the cloud has become the favorite choice to store data. In short, the cloud is the best place to store your private information.
However, like other technologies, cloud storage comes with certain security risks and threats. Therefore, users who depend on cloud storage should know about the vulnerabilities. That way, they can stay one step ahead of cybercrimes.
When it comes to managing cloud network security, you need to keep a lot of things in mind. From simple errors to serious cyberattacks, cloud computing poses severe threats. This post discusses cloud computing security risks and challenges you should know. Additionally, you will learn how to protect yourself from the vulnerabilities.
Cloud Computing Security Risk and Challenges
A CSP or cloud service provider such as Oracle Cloud or Google Cloud allows users to store and protect their sensitive data. However, relying on them blindly can make some users skeptical. After all, they do not have any idea how cloud computing works. Besides, they are not sure if the cloud service provider will protect their private files, videos, and photos.
In reality, cloud computing has innovative technology that can protect your professional and personal information efficiently. Cloud service providers can access strong cybersecurity technologies specifically designed for the cloud. However, businesses and individuals cannot get access to this technology. It safeguards your sensitive information from cyberattacks and malware.
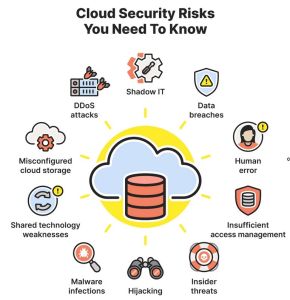
Although cloud-based systems can store your information without compromising security, they have their challenges, threats, and risks. Below listed are some of the popular cloud security problems you should know.
-
Data breach
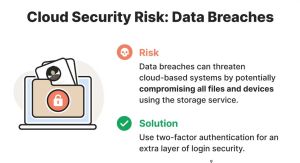
Information is the only thing that hackers or scammers are looking for. Intruders can steal plenty of information from one place, that is, from cloud service providers.
Data breaches happen when someone accesses the data without user consent. Data breaches have become a common issue because organizations and individuals are migrating to the cloud more than ever. As such, data breaches will prevail.
The massive amount of information that cloud service providers store for businesses and individuals invites data breaches. Seasoned cybercriminals looking for private information put cloud service providers at risk of users’ data.
-
Unprotected attack surface
“Attack surface” is a new term coined from cloud computing. Previously, data was stored in a single location. It was easy to create a secure data center.
However, cloud services removed the barriers because the cloud changes location. Besides, it is not clear who is responsible for the data and its current location. Traditional risk management, risk assessment, and asset discovery processes were in place when networks were more centralized and stable. These dated processes cannot keep up with the pace at which attack vectors and other vulnerabilities erupt in today’s cloud computing environment. This gives rise to the phenomenon called attack surface.
Lately, the attack surface increased by 67% as of 2022. Around 69% of attacks are the result of poorly or unmanaged assets. To put limitations on the attack surface, do the following.
- Categorize your information based on security and sensitivity
- Encrypt your sensitive data by using 2-factor authentication
- Find out who has access to your data
- Delete exposed or unused data stores
You need to keep the size of your data small so that you can manage each file with proper security.
-
Loss of data
Like office or home networks, cloud computing can become a victim of data loss. It happens because of data breaches, wide system malfunctions, or natural disasters. If you want to protect your information:
- Review the backup strategy provided by your cloud computing service. At least you are aware of how secure your digital assets are.
- Take appropriate steps for data backup by yourself. It ensures that your data is not destroyed completely.
-
Inadequate access management
Identity and access management allow access to data in the cloud. It has certain limitations.
- Who can access certain files
- From where users can access the files
- The devices allowed to access the files
Cloud security sets limitations on who can access information and from where. That way, the devices stay safe when connected to a network or create guidelines prohibiting users from connecting to public Wi-Fi hotspots. Hackers can use the information because of inadequate access management of stored data.
-
Hijack cloud account
Hijacking a cloud network is easy when there are inefficient security protocols and resources.
Cybercriminals can hijack a cloud account when they manage to control it. Cyber attackers use botnets or phishing scams to penetrate and infect the cloud-based account. This is how they gain complete control of the account. Hackers can steal information easily. If it is a business account, highly sensitive corporate or consumer files are at severe risk.
-
Shadow IT
If you are unaware of a threat, you cannot see it. The same goes for cloud computing security. Shadow IT is the data that is managed by an employee without proper approval from the concerned authority. This includes the following.
- Sharing tools based on Bluetooth
- Peer-to-peer tools
- Personal laptops, tablets, or phones
- Messaging apps
More recently, shadow IT has become a major issue because of the increased migration of users to cloud-based systems. Shadow IT exposes organizations to critical security risks that the IT department itself is not aware of.
-
Malicious infections

In today’s digital world, hackers can infiltrate and use information on cloud-based networks through several methods. One of the popular ways hackers often use is malware. The computer installs the malware without the consent of the user. Once installed, the malware takes complete control of the computer. It can damage the system or disrupt operations at will.
Cyber attackers who want to control your cloud account might use malware to fool the cloud network. It makes the cloud service believe that the malware is an integral part of the system. The malware works in cohesion with the cloud network to manipulate or destroy data whenever it wants.
-
Insider cyber threats
Different from inadequate access management, insider cyber threats typically refer to the individuals who can access a cloud network or account. In short, these users already have access to your data and can misuse them. They ignore cybersecurity rules that keep your information secure and private. Insider threats could be the files that your employees should not share outside a specific network. Or, it could be websites that you do not want your guests to visit.
Cloud network protection includes managing people who are within the network circle.
-
Weakness in shared technology
The PaaS (Platform as a Service) and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) technology systems connect to the cloud. As such, they can share the vulnerabilities that cloud security carries. Because of this, hackers can take advantage of the situation and exploit users’ information.
When a hacker gains control of a system within a network, they can likely hack other systems in the network. It might compromise users’ information.
-
Zero-day exploitation
The data center in an organization stores the information in a software application, computer network, or cloud. For example, the videos and photos stored in iCloud are stored on Apple-owned servers. This may give rise to zero-day exploits. Hackers can target the threats in popular computing systems and software that the vendor has yet to patch.
This kind of attack got its name because developers have been given zero days to mitigate the risks after detection. Protection against zero-day exploitation is difficult. Even an updated cloud configuration cannot stop cyberattacks.
-
Cloud storage misconfigurations
Cloud computing space is evolving continuously to counter emerging technical opportunities and eminent threats. Almost every business now adopts multi-cloud landscapes to benefit from different cloud service providers. However, the risks associated with misconfigurations have increased, too.
Misconfigurations in cloud computing are treated as cyber security risks. It refers to the errors, gaps, or glitches that arise during the process of cloud adoption. If an organization operates several cloud networks simultaneously, it becomes difficult to detect misconfigurations and resolve them. As of 2021, around 31% of misconfiguration issues surfaced. This is because of oversight and inadequate controls.
-
Compliance
When it is about safeguarding customer data and secure storage, organizations should comply with the prevalent regulation standards.
Whether it is HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act), or other types of regulatory authorities, an organization could land into deep trouble because of non-compliance.
-
Breach of data and privacy contract
Other than following the guidelines of government regulations, organizations should comply with data and privacy contracts with their users.
Typically, the contracts reflect how the businesses should store, share, and protect users’ data with other companies. Contract breaches occur when the customers’ information gets compromised while it is in the cloud. Any kind of violation can attract legal consequences. This impacts the company’s reputation and customer loyalty.
-
Unprotected APIs
APIs or application programming interfaces allow software components to interact with each other. However, the components should never know how they are integrated. Whenever you check weather updates, order an Uber, or send mobile payment, you are using an API.
When organizations or businesses secure their apps or software, certain APIs are overlooked. As such, they stay unprotected and increase the risk of vulnerabilities. API breaches are considered an eminent threat to the cyber world.
-
Human error
Hackers look for vulnerabilities so that they can launch their attacks with ease. Sometimes, users are unaware that their efforts for personal security have been compromised. In 2022, 82% of personal data breaches were the result of misuse and human error. A human error refers to the lack of action or unintentional actions that result in data breaches. Here are some scenarios.
- Communicate with the wrong recipient
- Use weak passwords
- The web-based app or software is not up-to-date
- Compromised IP address
- Downloaded malware unintentionally from dubious software
Hosting the information on public cloud networks increases security risks. When one system is compromised, every system on the network can become a victim of the attack.
-
DoS attacks
DoS (denial of service) attacks come bundled with a website so no one can access its resources. DoS attacks prevent cloud services by flooding the CPUs with lots of attack packets. As such, it makes the network unstable.
Because of this, computer operations halt. Besides, the network blocks access to files and documents until the connection is cleared.
-
Advanced persistent threat
APT or advanced persistent threats happen when a cyber-criminal builds an unauthorized connection within the network to mine information in the long run. Typically, APTs target big organizations. However, midsize and small businesses are equally targeted more often.
Protection against APTs is difficult because it is not possible to identify an intruder once they enter the network.
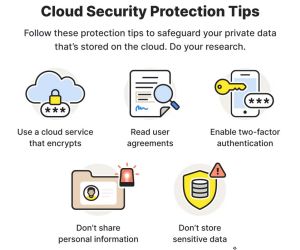
Cloud computing security protection tips
-
Choose an encrypted cloud service
Protection against cyber criminals involves taking strong steps. One of the best ways to counter cyber theft is to ensure that your cloud service has innovative tools. Choose a service that encrypts your data both on your computer and in the cloud. Strong encryption makes sure that the service admins, service providers, and third parties cannot access your information.
-
Pay attention to user agreements
It is unwise to sign up for a cloud service provider without reading their user agreement. The agreement gives you an insight into important information regarding the service on offer. You can know if the service offers complete data protection. Also, you can know if they can sell or use your information when signing up for the service.
Never give your consent on anything without a proper understanding of every point mentioned in the agreement. Whenever the provider modifies their privacy policies, they should send you an alert when logging in. They should send notifications via text or email. Make sure you read those notifications to know if the changes impact your information.
-
Activate 2-factor authentication
If your provider offers a 2-factor authentication, you should use it. That way, it protects cloud privacy and security. A 2-factor authentication requires a user to provide additional information other than a password. Here are the common methods to authenticate a user.
- Security questions
- Biometric logins
- Authenticator apps
- One-time codes
- PIN code
Not every cloud account will ask for additional information during log-ins. Hence, check the settings to know if you have the 2-factor authentication feature.
-
Never share personal data
Certain personal information might appear unimportant to you. However, if a hacker knows the information, your identity could be compromised. Never provide information publicly because hackers might use it to answer security questions. Below are some examples.
- Your date of birth
- The name of your mother
- Your street name where you grew
- Your pet’s name
- The name of the place where you met your life partner
Some cloud service providers give you the option to set questions of your choice to answer during verification. In that case, try using questions and answers you know and others do not. For example, your childhood nickname you are embarrassed of. Or, the name of the place from your first vacation.
-
Never store sensitive information
It is not a good idea to store sensitive data on the cloud. Or else, you may face embarrassment or blackmail if an intruder gets the information. Maintain caution when storing information such as financial statements, IDs, or Social Security numbers. There could be other kinds of sensitive information that you should keep in mind when storing them on the cloud.
It is better not to store intimate pictures or interactions in the cloud. If you do not want others to see your diet progress pictures, never store them on the cloud.
-
Do thorough research
It is important to do thorough research before storing your professional or personal data on the cloud. Have a clear understanding of the services provided by your cloud provider. This helps you lower the risks of becoming a victim of cybercrimes. You need to know who can access your data, what security protocols the cloud has, and who is responsible for cloud data security.
Safely Navigate the Cloud
Cloud computing allows you to access your data with ease from anywhere. Still, your online safety could be jeopardized because of the risks associated with cloud security. Protect yourself from these security issues by following useful tips. That way, you can manage your files, photos, and documents efficiently.
Prevent your information from falling into the wrong hands by using robust cloud security software. Using strong protection against data breaches, malware, and hackers, your valuable data stays good.